Ecommerce is a booming market. Some experts predict it will surpass $2 trillion over the next few years.
There are a lot of opportunities to get your piece of the pie, if you know how to market your ecommerce business the right way.
SEO is the best way to get your ecommerce site in front of people who are already searching to buy. Here’s a quick checklist to optimize your ecommerce site for SEO success.
Keyword research
Keyword research can be difficult for ecommerce sites. You’re trying to promote product pages, not informational content like keyword-optimized blogs.
But there are some tools out there that can help you find relevant keywords with high purchase intent.
Keyword Planner
Google Adwords Keyword Planner is meant for advertising keyword research, but these high-purchase intent keywords are relevant to ecommerce SEO as well.
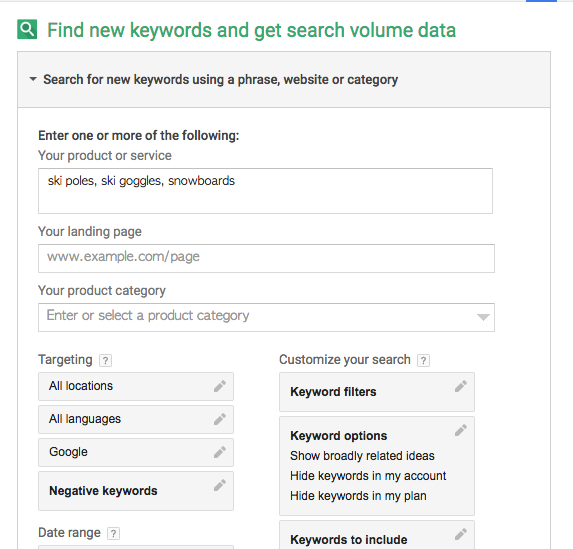
Sign up for Google Adwords. In Keyword planner, click “Search for new keywords using a phrase, website or category.”
Then type in a few base keywords for your products, separating each by a comma:
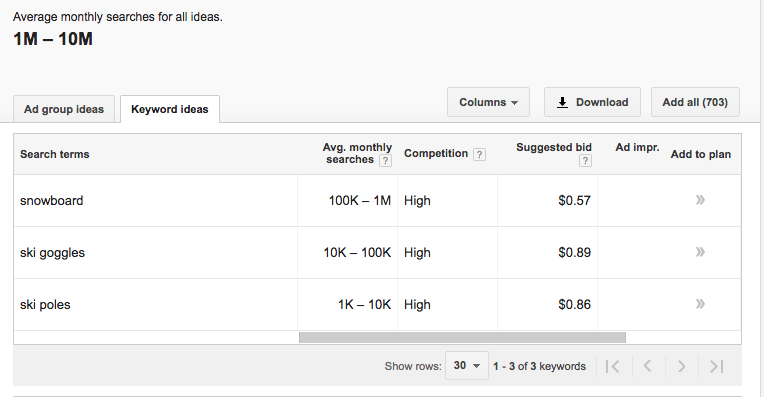
Keyword Planner will show you the average monthly searches of your keywords and suggest related keywords to help you expand your list.
Amazon
Amazon is the granddaddy of ecommerce sites. Yes it’s your competitor, but it’s probably one you should emulate.
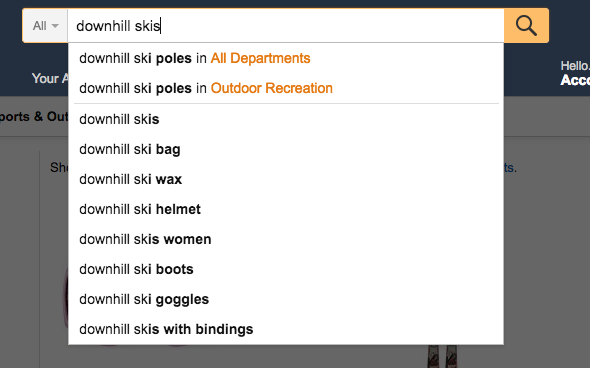
Use Amazon’s search suggestions to find keywords related to your products.
Just head on over to the search bar and type in a base keyword:
You can also take the suggested terms back to Keyword Planner to see their search volume.
Long-tail keywords (keywords with 2-5 words) will have lower search volume than base keywords, but they’ll also have less competition. Targeting long-tail keywords makes it easier to rank in search results.
On-Page SEO
Once you have your keywords, you need to optimize your content – which is a lot more work than just including keywords in the body text.
Your keywords should appear in the:
- Page title
- URL
- Body content
- At least one subheader
- Page copy (your product descriptions)
- Image alt tags
- Image file names
- Meta description
If you’re new to SEO, I recommend using a site plugin like SEO by Yoast or WebTextTool. These will analyze your content and make suggestions to improve your on-page SEO.
URL Structure
URL structure is complicated for ecommerce sites because of product categories. Many site owners opt to include categories in their URL structure, making their URLs very long:
This is a problem for SEO, because shorter URLs tend to rank better in search results. Longer URLs reduce the power of the keywords you use.
Some other ecommerce sites opt for product ID URLs:
www.yoursite.com/productID.123456789
That’s no good either, because you’re not taking advantage of your keywords for SEO at all.
The best option is to remove categories and product IDs from your URLs entirely, and just focus on your target keyword:
www.yoursite.com/9-west-flats
Schema Markup
Schema markup is an important part of any ecommerce site’s SEO strategy. Schema markup is extra information you add to your HTML to help Google understand your page content.
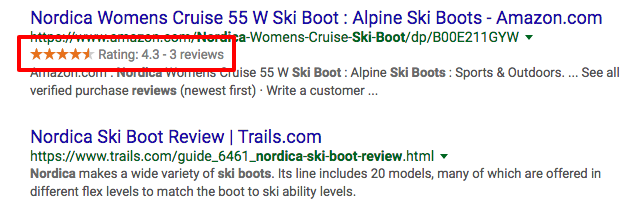
Google uses this information to create rich snippets in search results:
Markup your products so that Google might include extra details in search results, such as the price, reviews, and other helpful information.
Now, schema markup isn’t a rank factor – but it can help improve your clickthrough rate, which does affect SEO.
You don’t have to be an HTML expert to do schema markup.
Google has a Structured Data Markup Helper tool to help you create it. Then, you can use the Structured Data Testing Tool in Search Console to make sure you did it right.
Site Structure
How your site is set up can have a big impact on usability.
You want users to be able to navigate your site as easily as possible. That means minimizing how many clicks are necessary to navigate from your home page to a product page on your site.
Making sure your site users don’t get frustrated with your site navigation matters for SEO, as well. A good site structure will increase clickthrough rate and decrease bounce rate, which are both important search rank factors.
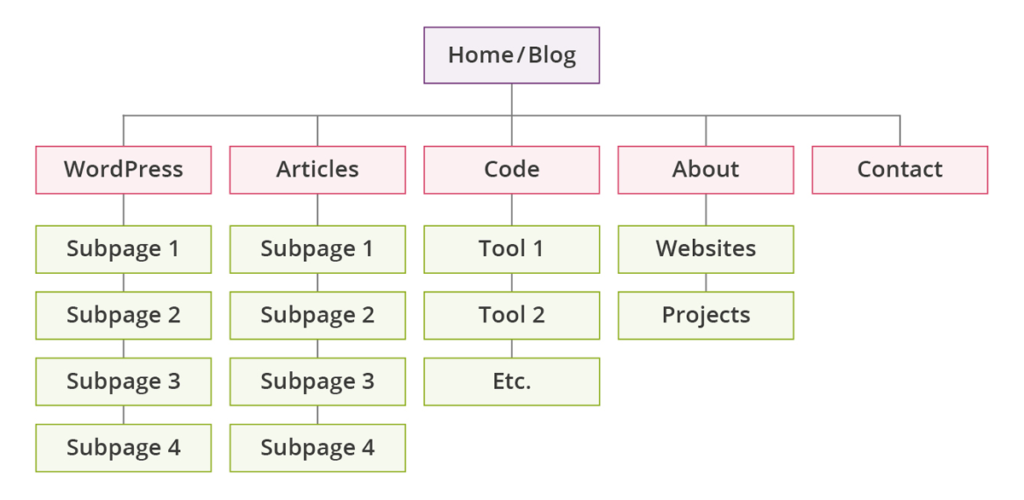
First, use a tool like Omnigraffle or Lucidchart to make a diagram of your current site structure.
You’ll see a tree navigating to your various categories, subcategories, and pages. Try to make this architecture as flat as possible.
If you have a series of subpages trailing off on their own, look for ways to integrate them back into the base structure.
Mobile Optimization
Ever since Google rolled out the Mobile-Friendly Update (AKA Mobilegeddon), mobile optimization has been an important rank factor.
Sites that are designed for use either on or off mobile are given a rank boost in mobile search results – so make sure your site has a responsive design to reap the benefits.
Just head over to Google’s Mobile-Friendly Tool to see for yourself:
Internal Links
You already have a series of internal links as part of your site structure. You can do more to optimize them for SEO, as well.
Optimize your anchor text
Google uses anchor text (the words in your hyperlinks) to determine what a page is about.
To optimize your internal links, you should include some of the target keywords when you link from one page to another. But only do it where relevant.
If you over-optimize your anchor text with keywords to the point where it looks unnatural, Google will notice. They might end up penalizing you for it.
So make sure you use a healthy variety of keywords in your anchor text, and only when it makes sense to do so.
Link from high-authority pages
Get strategic by linking high-authority pages to your product pages.
Say you have a blog post with lots of backlinks, or another page that ranks on the first page of search results. Link these pages to your product pages to get more “link juice” for other areas of your site.
External Link Building
Links are one of Google’s top three rank factors. Google looks at the number and quality of links pointed at a page from other sites to help determine search rank.
If you want a fighting chance to rank well, you’ll need to develop a link-building strategy.
Here are a couple of opportunities you can find to build links for your ecommerce site:
Press mentions
Sign up for Help a Reporter Out (HARO). This tool will send you daily notifications of journalists looking for sources for their stories.
Where relevant, respond to the queries to be considered as an expert source. If a journalist interviews you for their piece, it could help you get links back to your site from high-authority news sites.
Product reviews
Finding high-authority bloggers to write a review of one of your products can help you get links pointed at specific product pages. Reach out to your current customers via email to see if they’re willing to review your products on their blogs.
Search algorithms change all the time, and SEO strategies need to change with them. But follow this quick checklist and you’ll be well on your way to great ecommerce SEO.
Image Credits: Pixabay, Pixabay